In this article we present an RGB LED example on a Raspberry Pi Pico, rather than just use the default example to flash an LED, we will connect an RGB led up to.
Tri-color LEDs contain three different LED emitters in one case. Each emitter is connected to a separate lead so they can be controlled independently. A four-lead arrangement is typical with one common lead (anode or cathode) and an additional lead for each color.
Others, however, have only two leads (positive and negative) and have a built-in electronic controller.
I used an RGB LED module, I find this is easier than using a breadboard with an RGB led and required resistors but you construct this if you want, the layout later in the article shows how to make this.

Parts List
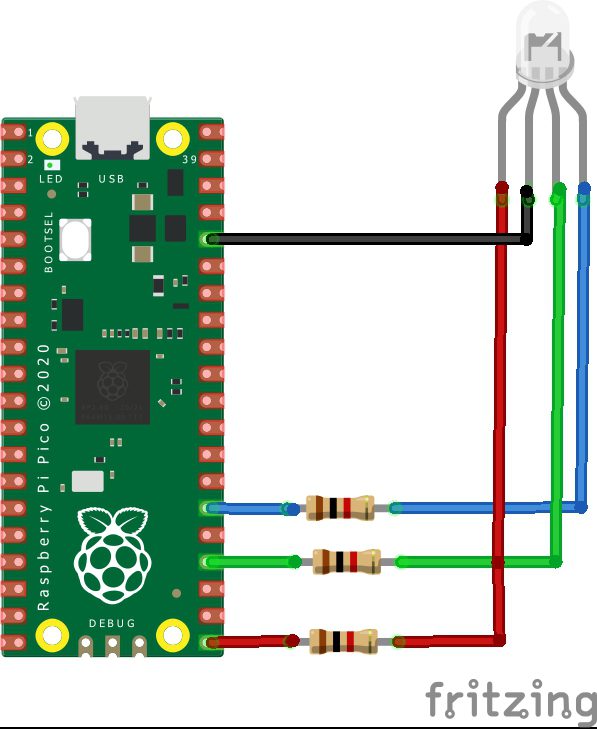
I used an expander board with the raspberry pi pico fitted to it but you can quite easily connect and RGB led directly to the board with cables. The layout that you can see underneath in the article shows this.
Here are some basic parts
| Name | Link |
| Raspberry Pi Pico | Aliexpress |
| RGB Board | Aliexpress |
| Connecting cables | Free shipping Dupont line 120pcs 20cm male to male + male to female and female to female jumper wire |
Layout
The schematics and layout shows 3 1K resistors, this is what my small module which you can see pictured above had built in. These are the individual components if you want to build this using individual components.
Code
I used the thonny IDE that supports Micropython on the Raspberry Pi Pico
The machine module is used to control on-chip hardware. This is standard on all MicroPython ports. Here we are using it to take control of a GPIO, so we can drive it high and low
We also include the utime module to bring in a basic delay
We then set the various pins to outputs like – red = Pin(18, Pin.OUT)
Now as we said this is a common anode rgb led, so to switch an individual led on you send a low (0) and to switch an led off you send a high (1). If you have a common cathode type the you need to reverse this.
So to switch the red led on you would send this – red.value(0)
To switch the red led off you would send this – red.value(1)
This first example switches all of the led off then back on again.
from machine import Pin
import utime
red = Pin(16, Pin.OUT)
green = Pin(18, Pin.OUT)
blue = Pin(20, Pin.OUT)
while True:
red.value(1)
green.value(1)
blue.value(1)
utime.sleep(1)
red.value(0)
green.value(0)
blue.value(0)
utime.sleep(1)
This example switches the red led, green led and blue led off in sequence
from machine import Pin
import utime
red = Pin(16, Pin.OUT)
green = Pin(18, Pin.OUT)
blue = Pin(20, Pin.OUT)
while True:
red.value(1)
green.value(1)
blue.value(1)
utime.sleep(1)
red.value(0)
green.value(1)
blue.value(1)
utime.sleep(1)
red.value(1)
green.value(0)
blue.value(1)
utime.sleep(1)
red.value(1)
green.value(1)
blue.value(0)
utime.sleep(1)